Data is often stored in stacked (long) or record (wide) format.
DataFrame表的重组,长表变宽表 和 宽表变长表。
什么是长表?什么是宽表?这个概念是对于某一个特征而言的。例如:一个表中把性别存储在某一个列中,那么它就是关于性别的长表;如果把性别作为列名,列中的元素是某一其他的相关特征数值,那么这个表是关于性别的宽表。
pivot()之后能得到一个宽表,melt()之后能得到一个长表。
pivot() and pivot_table() 长变宽
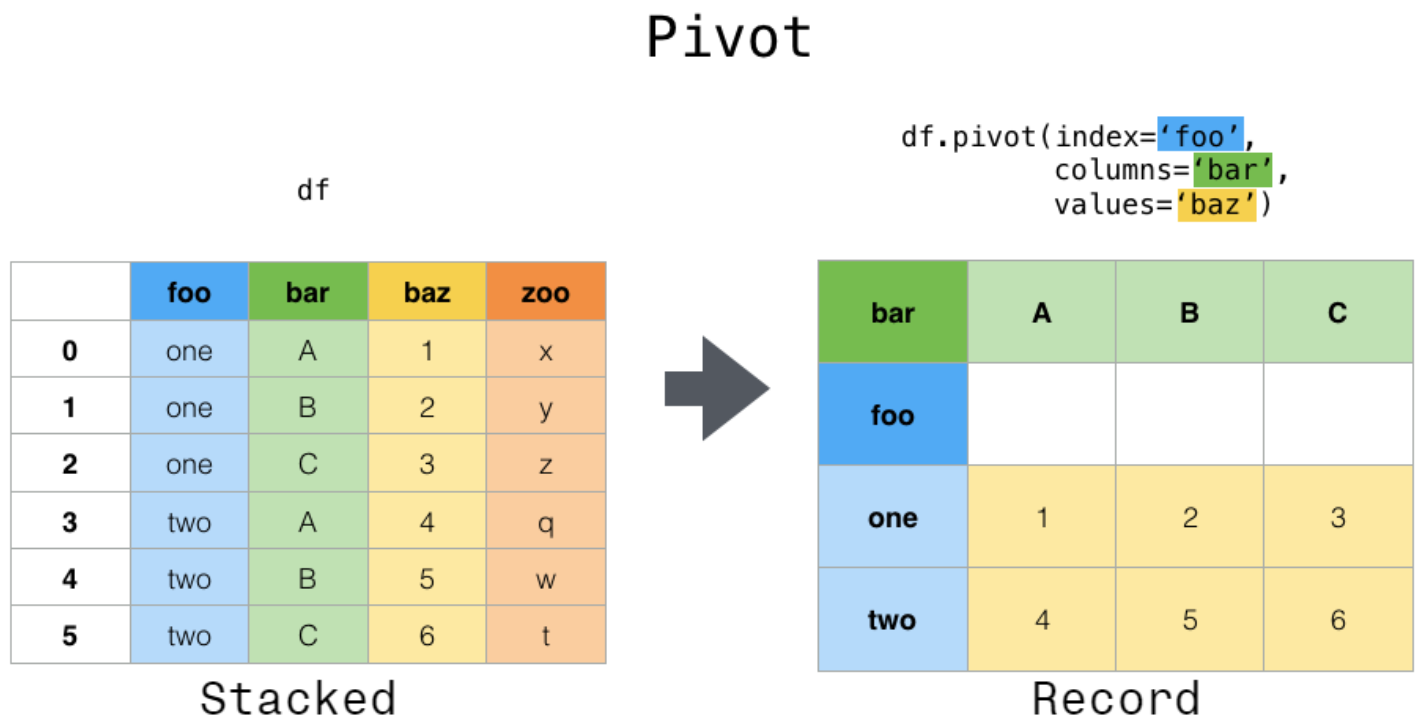
long => wide
Return reshaped DataFrame organized by given index / column values.
Reshape data (produce a “pivot” table) based on column values. Uses unique values from specified index / columns to form axes of the resulting DataFrame.
对于一个基本的长变宽操作而言,最重要的有三个要素,分别是变形后的行索引、需要转到列索引的列,以及这些列和行索引对应的数值,它们分别对应了pivot方法中的index, columns, values参数。新生成表的列索引是columns对应列的unique值,而新表的行索引是index对应列的unique值,而values对应了想要展示的数值列。
1 | |
1 | |
pivot() can only handle unique rows specified by index and columns. If you data contains duplicates, use pivot_table().
pivot的使用依赖于唯一性条件,那如果不满足唯一性条件,那么必须通过聚合操作使得相同行列组合对应的多个值变为一个值。
melt() and wide_to_long() 宽变长
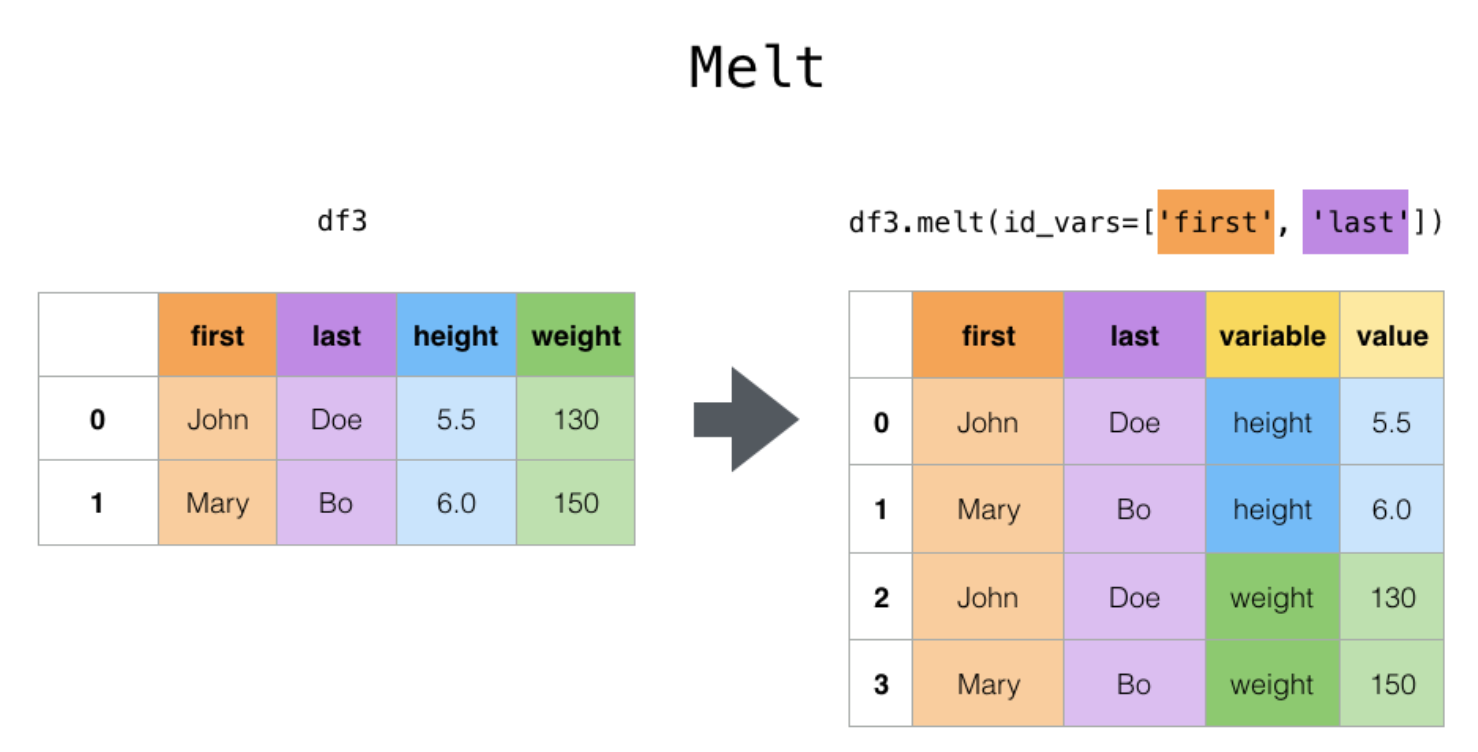
wide => long
Useful to massage a DataFrame into a format where one or more columns are identifier variables (id_vars), while all other columns, considered measured variables (value_vars), are “unpivoted” to the row axis, leaving just two non-identifier columns, “variable” and “value”. The names of those columns can be customized by supplying the var_name and value_name parameters.
1 | |
1 | |
References:
- https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/user_guide/reshaping.html#reshaping
- https://pandas.pydata.org/docs/user_guide/reshaping.html#reshaping-melt
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/352885638